Content Management Systems: What is the Right Platform For You

Understanding Content Management Systems (CMS)

Using a CMS, you can handle content creation, management, editing, and publishing through an easy-to-use interface. You can personalize your website’s design and features by obtaining templates and extensions, rather than coding from scratch. The CMS allows multiple users to collaborate on the same platform in the background, among other capabilities.
If you’re curious about how a single software accomplishes all these tasks, let’s explore the inner workings of a CMS.
How CMS Works
Let’s begin with content creation. Without a content management system, you’d have to craft a static HTML file and then upload it to your server, which might sound rather complex.
However, when you have a content management system like WordPress, you can simply compose your content within an interface that closely resembles Microsoft Word:
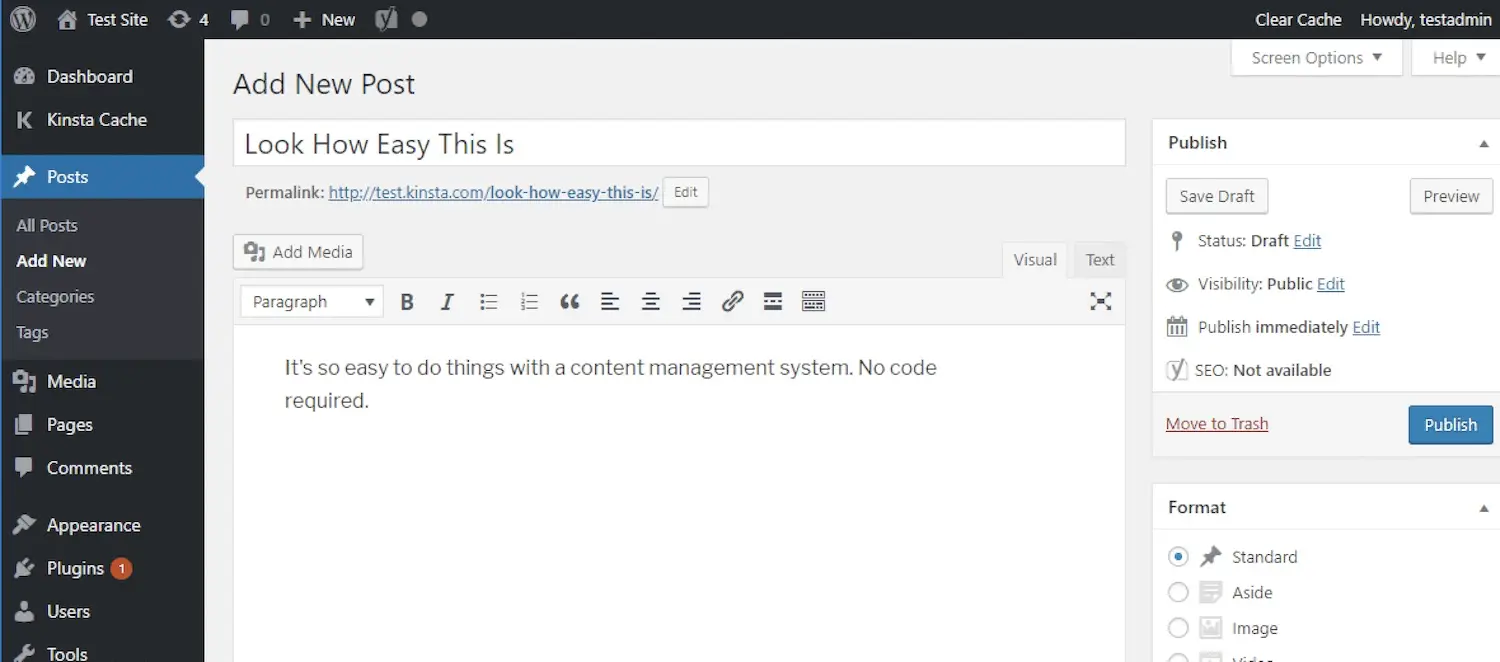
Likewise, for uploading and handling media, such as images, you can effortlessly navigate the media library instead of having to directly engage with your web server:
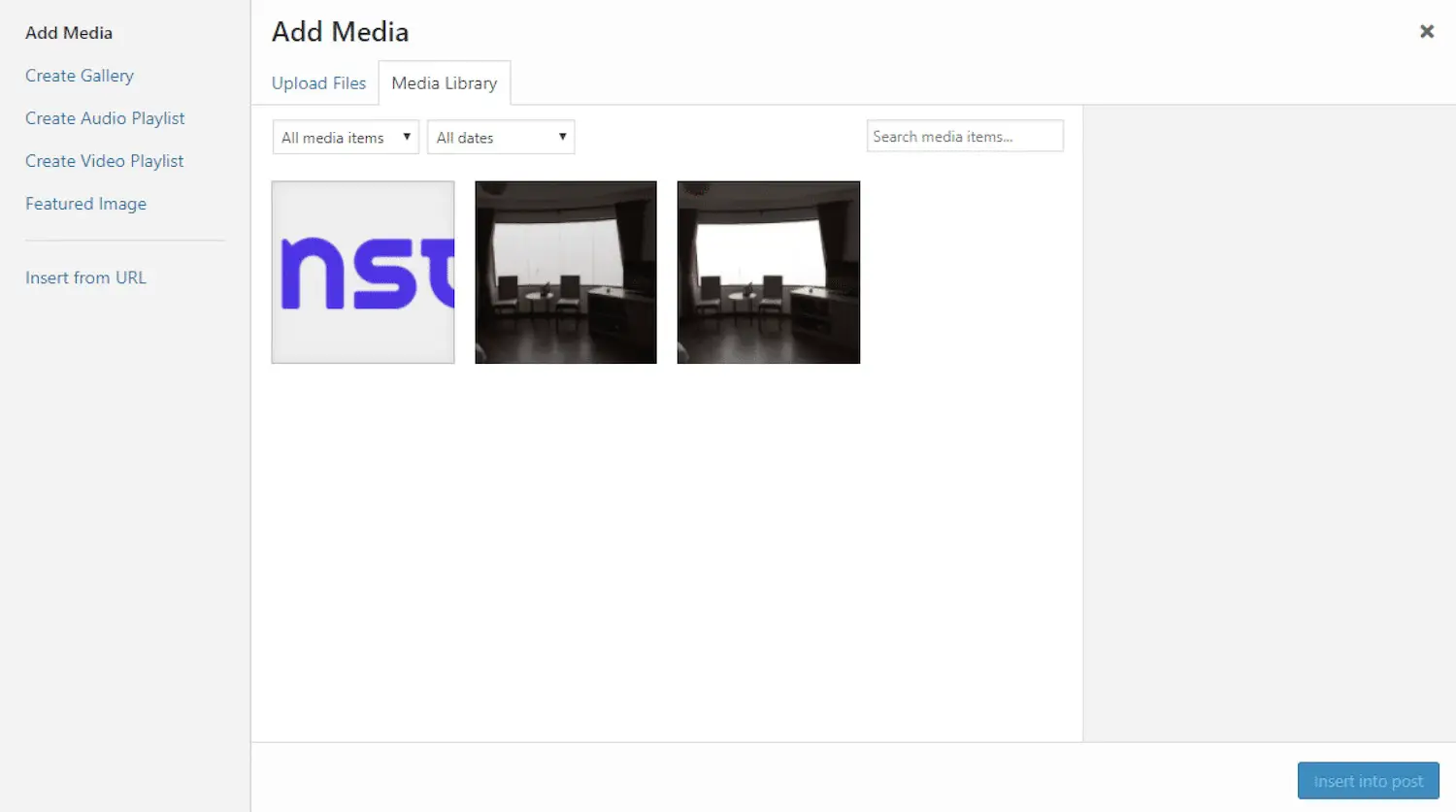
How to Use a CMS

Instead of beginning with a blank HTML page, you can open the content editor. Here, you can easily format text, include links and calls to action (CTAs), and insert images and tables by simply dragging and dropping modules or clicking a few buttons, without the need to write HTML, CSS, or JavaScript from scratch.
For making other adjustments to your website, such as modifying the permalink structure or adding extensions, you can simply navigate to the relevant section in your admin panel. This is where the content management application (CMA) comes into play, as all these changes occur within an easy-to-use interface that shields you from the underlying code.
Once you’ve completed your modifications, the content delivery application (CDA) steps in. It takes the content you entered in the CMA, compiles the code, presents it to your website’s front-end visitors, and stores it. This means that when you want to publish a new blog post, for instance, you just need to click the Publish button, rather than manually uploading a page to your server.
Now that we’ve covered what a CMS is, how it functions, and how to utilise it, let’s explore the advantages of using a CMS compared to building a website from the ground up or using another website building tool.
Benefits of Using CMS

1. No Coding Expertise Needed
2. Effortless Collaboration
3. User Roles and Permissions
In the absence of a CMS, you would need to write complex code, including intricate conditions and checks in JavaScript, to establish user roles and permissions.
4. SEO Tools and Add-Ons
CMS platforms come equipped with in-built features and additional tools to enhance your website’s search engine Optimisation (SEO). You can utilise these features, whether built-in or third-party, to:
● Customize page titles and meta descriptions
● Opt for SEO-friendly URL structures
● Generate XML sitemaps
● Include image alt text
● Create 301 Redirects
● Implement breadcrumb navigation
● Enhance page loading speed
Following these SEO best practices will increase your likelihood of achieving better rankings on major search engines like Google.
5. Security Measures and Extensions
6. Pre-designed Templates
For instance, opting for a responsive template ensures that your site appears well on any device without the need for extensive coding. Templates not only save you time during the design phase before your site’s launch but also streamline future website redesigns, making them faster and more straightforward.
7. Effortless Updates
8. Blogging Capabilities
A significant advantage of using a CMS is that most offer built-in blogging functionality or extensions, simplifying the process of creating and publishing blog content and reaping its benefits.
9. Content Scheduling
With a CMS, scheduling content is as simple as clicking a button. Most platforms support scheduling not just for blog posts but also for website pages, landing pages, and emails. For example, CMS Hub allows you to schedule blog posts, website pages, landing pages, and emails with ease.
10. Convenient Accessibility
Moreover, most CMS systems offer a unified dashboard or control panel where you can conveniently access your site’s content, theme, plugins, settings, and various other elements all in one location.
Examples of CMS
● WordPress
● Drupal
● optimizely CMS
● Contentful
● Squarespace
● Wix
It’s worth noting that while platforms like optimizely Monetize, Adobe Magento, and Shopify manage content like a CMS, they are primarily considered eCommerce platforms with additional content management features rather than being classified as traditional CMS platforms.
The Future of CMS






